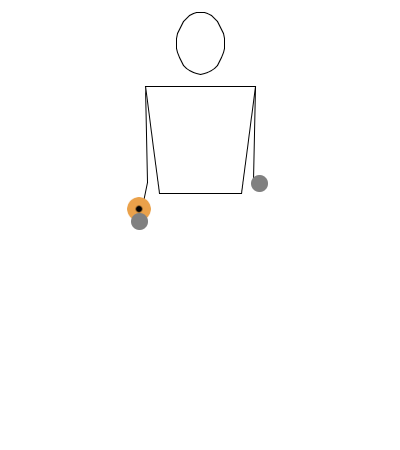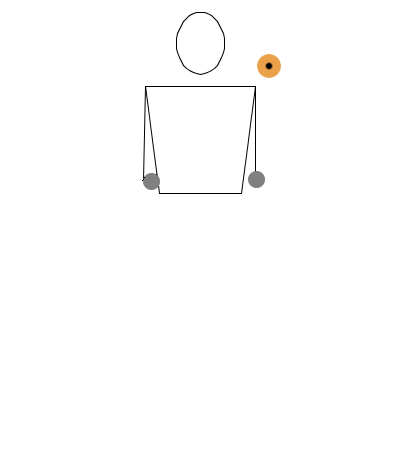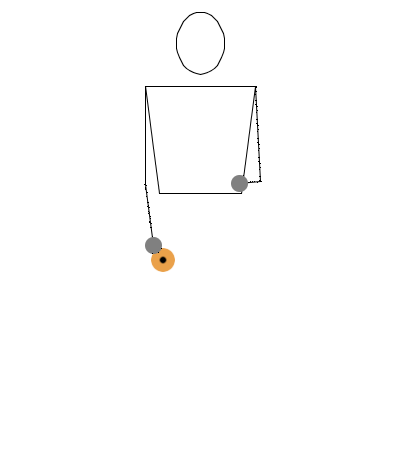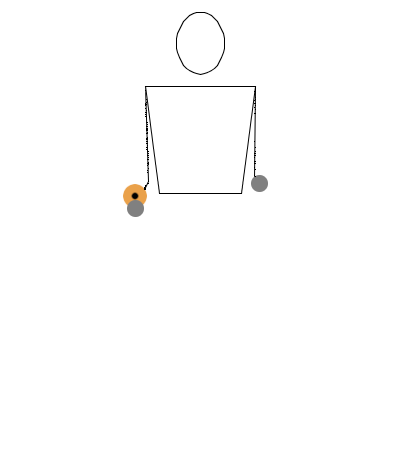
This notation is essentially a translation of the bouncing ball notation applied to diabolo. We will use the common understanding that when the diabolo is on the string, it behaves as if it’s on a controlled surface, similar to how a ball behaves when rolled on a table or bounced on the ground.
Asyncronich Notation
0 . Nothing inside of the string.
1 . The diabolo goes directly from one side of the string/hand to the other.
2 . Retention of the diabolo in the string, stick, or hand.
3 . The diabolo goes through the air from one side of the string/hand to the other and it spends in the air the time of three ones.
4. The diabolo is thrown to the same side of the string and it spends in the air the time of four ones.
5. The diabolo goes on the air from one hand to the other and it spends in the air the time of five ones.
6. The diabolo is thrown to the same side.
etc…
Syncronich Notation
In the syncronic notation we throw and catch the diabolos simultaneously and we must write de siteswap in between brackets like that (left throw, rigth throw). Also in the syncronic notation we do not use odd numbers. We put an x after the number to say that that throw crosses.
To explain this notation I will write only the throws of the left hand.
(2,0) . The diabolo stays in one side of the string.
(2x,0) . The diabolo goes from one hand to the other through the air.
(4,0) . The diabolo is thrown to the same side of the string and it spends in the air the time of four ones.
(4x,0). The diabolo goes from one side of the string to the other by the air.
etc..
Specific notation for the string
B — Bounce the throw off the floor. The format is to put as many B’s as you want bounces, followed by the style of the bounce:
BL or L for lift bouncing
BF or F for force bouncing
BHL or HL for hyperlift bouncing (for a description of hyperforce/hyperlift bouncing, see this discussion on rec.juggling)
BHF or HF for hyperforce bouncing
Usually we will use BF or F because when we recive the diabolo from the air, we force it to enter in the string but there are some patterns where it is useful only to use B, like in the 3 diabolos Low Cascade.
You can find more information about the specific notation here
Asinch String Notation for the string [ _F ]
1F . Diabolo goes from one side of the string to the other.
2F . Retention of the diabolo in the string.
3F . The diabolo goes by the string from one hand to the other and it spends in the string the time of four ones.
4F . Retention of the diabolo in the string and it spends in the string the time of four ones..
5F . Retention of the diabolo in the string and it spends in the string the time of four ones..
etc…
Sinch String Notation for the string ( _F )
(2xF,0) . The diabolo goes from one hand to the other by the string (2 Diabolo Low Synch rythm, or the Diabolo that goes on the rope in High)
(2xF,0) . The diabolo goes from one hand to the other by the string (2 Diabolo Low Synch rythm, or the Diabolo that goes on the rope in High)
(4F,0). Diablo goes from one side of the string to the other by the string. ( 3 Diabolo Synch Low Rythm)
(4xF,0). Diablo goes from one side of the string to the other by the string. ( 3 Diabolo Synch Low Rythm)
etc..
*** Folowing you can see some examples ***
*** All the examples are done with JugglingLAB ***